Bihar Finance Minister Vijendra Yadav presented the 2026-27 budget of over ₹3.47 lakh crore in the Bihar Legislative Assembly. The government stated that the goal is to make life easier for all sections of society. The state's growth rate is projected to be 14.9%. The Nitish government has described it as a budget that will further the goal of a "developed Bihar." Chief Minister Nitish Kumar posted on social media, saying that this budget is based on the principle of "development with justice," taking into account every section of society – farmers, youth, women, entrepreneurs, and poor families.
Key Features of the Budget:
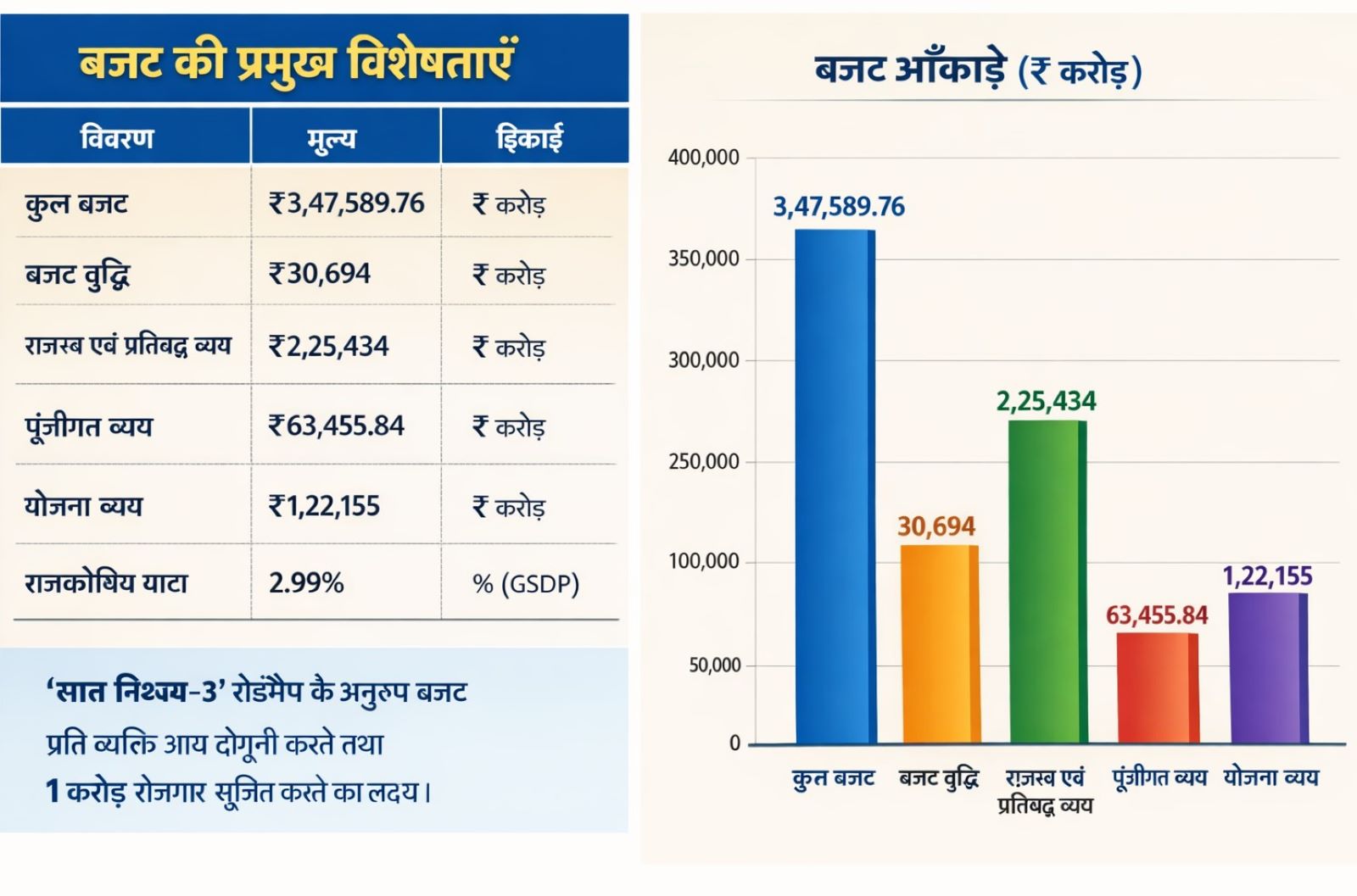
• Total
Budget: ₹3,47,589.76 crore, the highest in Bihar's history.
• Increase
in Budget Size: An increase of approximately ₹30,694 crore compared to the
financial year 2025-26.
• Revenue
and Committed Expenditure: ₹2,25,434 crore (approximately 65%).
• Capital
Expenditure: ₹63,455.84 crore (approximately 18.26% of the total).
• Plan
Expenditure: ₹1,22,155 crore (approximately 35%).
• Fiscal
Deficit: Estimated at approximately 2.99% of GSDP.
• Budget aligned with the 'Seven Resolves-3' roadmap: Aiming to double per capita income and create 1 crore jobs.
Key Points
1. Education:
The education sector received the highest allocation of ₹68,216 crore,
prioritizing school education, teacher support, infrastructure, and quality of
learning. Model schools will be established in every panchayat to promote
quality education.
2. Women
Empowerment and Social Welfare: The budget emphasizes supporting 1.56 crore
women through self-help groups and related welfare schemes.Social welfare
provisions include ₹7,724 crore for schemes benefiting women, children, the
elderly, and vulnerable sections of society.
3. Agriculture
and Farmers: Enhanced Support: Eligible farmers will receive ₹9,000 per year
under the 'Jannayak Karpoori Thakur Kisan Samman Nidhi', which is ₹3,000 more
than before.
4. Employment
and Jobs: Under 'Saat Nishchay-3', the goal is to create 1 crore employment
opportunities by 2030. A special provision has been made for financial
assistance of up to ₹2 lakh to every eligible woman under the Chief Minister
Women Employment Scheme. Skill development centers will be established on a
hub-and-spoke model to develop employment-oriented skills.
5. Infrastructure
and Connectivity: Major infrastructure projects have been announced, including
five new expressways, improved road networks, and urban development. Work is
underway on airport development and regional air connectivity projects.
6. Health
and Medical Services: The budget strengthens healthcare services with
provisions for upgrading hospitals and expanding medical facilities. Provisions
have been made to increase the number of beds at PMCH and establish new medical
colleges in additional districts.
7. Industry
and Investment: The new industrial policy aims to attract large-scale
investment and strengthen private sector participation. Measures have been
taken to attract private investment of up to ₹50 crore in the industrial
sector. The revival of closed sugar mills has been provided for under the
Industrial Support Mission. Claim to develop urbanization in accordance with
national standards: The state government has stated that it is committed to
promoting urbanization in accordance with national standards. Currently, Bihar
has 19 municipal corporations, 89 municipal councils, and 156 nagar panchayats.
The government aims to develop all these urban bodies to make cities more
beautiful and provide citizens with basic and improved facilities.
8. Progress
of urban housing under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana: Under the Pradhan Mantri
Awas Yojana (Urban), a total of 4,18,394 houses have been sanctioned so far. Of
these, 1,75,249 families have been provided with permanent houses. The budget
describes this scheme as a significant initiative towards providing housing
facilities to the urban poor.
9. Sewerage
Infrastructure in Ganga Cities under Namami Gange Scheme: Under the Namami
Gange scheme, 39 STP and sewerage network projects have been sanctioned for 22
out of the 24 Ganga cities in the state at a cost of Rs. 8,426.01 crore. Of
these, construction work on 24 projects has been completed. The government says
that this will strengthen the cleanliness of the Ganga river and urban
sanitation systems.
10. Focus
on Solid Waste Management and Waste-to-Energy: Under the Swachh Bharat Mission
(Urban), an Integrated Solid Waste Management project has been approved on a
PPP mode for the management of solid waste generated from Patna city and 12
surrounding urban local bodies. This project also includes a provision for
electricity generation from waste. In addition, for the processing of solid
waste in 261 urban local bodies of the state, MRF plants with a capacity of
2938 TPD, compost plants with a capacity of 3387 TPD, a biomethanization plant
of 100 TPD, and sanitary landfills with a capacity of 1311 TPD have been
sanctioned.
11. Status
of Schemes under Smart City Mission: A total of 122 schemes were sanctioned
under the Smart City Mission in Patna, Biharsharif, Bhagalpur, and Muzaffarpur.
Of these, work on 101 schemes has been completed. The government says that
these schemes have improved urban infrastructure and services.
12. Investment
in Transport and Public Infrastructure: Of the 43 bus stand construction schemes
sanctioned to improve the transport system in urban local body areas,
construction work on 34 has been completed. Along with this, the Samrat Ashok
Bhavan scheme, a multipurpose building project, has been sanctioned in 143
urban local bodies of the state, of which construction work on 44 buildings has
been completed.
13. Facilities
for Street Vendors and Women: To facilitate street vendors, the construction of
66 vending zones has been sanctioned in urban local bodies. Of these, 25
vending zones have been completed. Meanwhile, keeping in mind the convenience
of women, a total of 105 Pink Toilet construction projects have been sanctioned
in 20 urban local bodies of the state.
14. Patna
Metro and Urban Transport: Work is underway on the 32.50 km long Patna Metro
Rail project for a fast and organized transport system in Patna city. Metro
rail operations have already commenced on 3.45 km of this stretch since October
6, 2025. The government believes that this will provide relief to the city's
traffic system.
15. Comprehensive
Urban Development and Other Schemes: Under the Chief Minister's Comprehensive
Urban Development Scheme, a total of 3,208 schemes have been sanctioned in
various urban local bodies of the state at an estimated expenditure of Rs.
2,091.90 crore. Under the Seven Resolves of Self-Reliant Bihar - Part 2, work
has been completed on 10 of the sanctioned crematorium construction projects in
41 cities and important river ghats. In addition, 38 storm water drainage
schemes have been sanctioned at a cost of Rs. 3,559.95 crore to address the
problem of waterlogging in urban areas.